Zarzaitine Fm
Type Locality and Naming
First described from the Zarzaitine field area of eastern Algeria by Lapparent & Lelubre, 1948. Part of the Continental Intercalaire.
References: Lapparent & Lelubre, 1948; Lefranc, 1958, 1991; Goudarzi, 1970; Assaf et al., 1976; Hallet, 2002, 2016; Tawadros, 2011; Shaltami et al., 2018.
Lithology and Thickness
Predominantly silty in character.
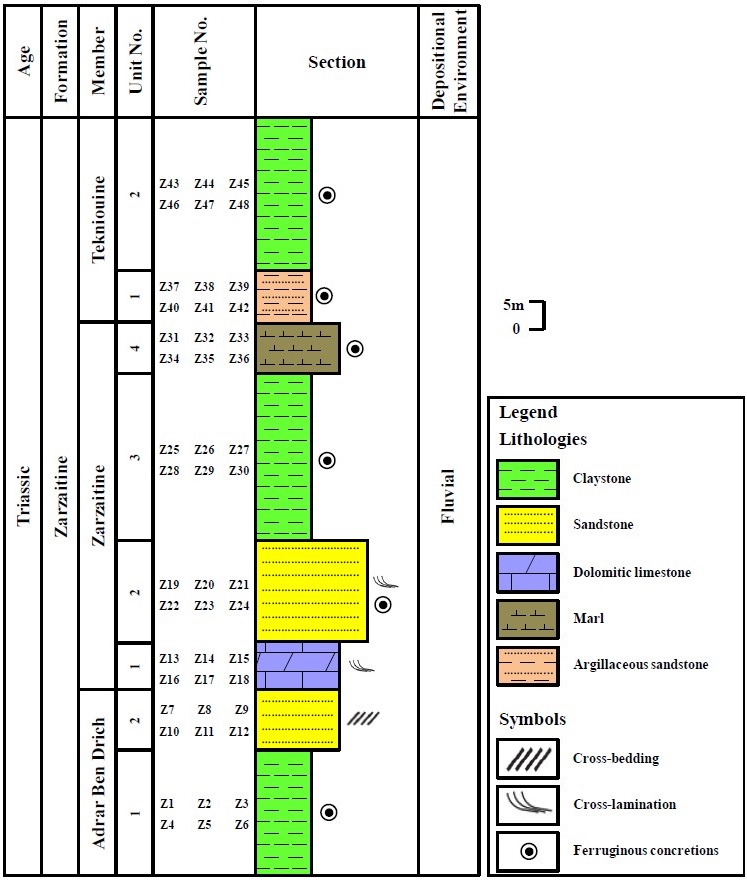
- In the Zarzaitine Field in Algeria, the Formation was divided into three informal Members by Lefranc (1958, 1991): Lower unit (Adrar Ben Drich Member) of multi-colored claystone and fine-grained sandstones containing Triassic dinosaur remains; Middle unit (Zarzaitine Mbr) of mottled claystone, argillaceous limestones and dolomites, with thin bands of gypsum and anhydrite; and an Upper unit (Tekniouine Mbr) of friable, argillaceous sandstones, claystones, dolomites and gravels.
- In Libya (Figure), it is composed of alternating bands of gypsiferous and ferruginous claystone, dolomitic marls, micaceous siltstones, and quartzose sandstones and gravels, with a distinctive brown color. The threefold division was not adopted. Uranium minerals were also discovered by Assaf et al. (1976) in the Zarzaitine Formation in Al Awaynat-Serdles area, Murzuq Basin, SW Libya.
Thickness: 400 m at the Type Locality. Varies from 75 to 150 m thick in southern Murzuq and Djado Basins due to erosion.
[Figure. Composite columnar section of the Zarzaitine Fm in the Tahughatin area, SW Libya. (Source: Shaltami et al., 2018).]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Underlying unit is the Tiguentourine Fm on the eastern side of the Djado Basin. On the western/southern sides of the Djado Basin, it may be in direct contact with the Dimbabah Fm.
Upper contact
Top is an erosional contact marked by a lateritic horizon, 3-4 m thick, indicating an important sedimentation break before the deposition of the overlying Taouratine Fm.
Regional extent
GeoJSON
Fossils
The Formation contains abundant fresh-water shelves, calcitized fossil logs up to 5 m in length, and rare dinosaur and reptile bones.
Age
Depositional setting
Continental. Includes braided-stream, alluvial plain, and lacustrine facies.
Additional Information